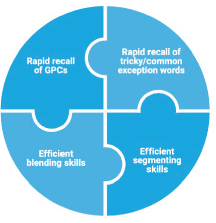
What is phonics?
Phonics is a way of teaching children how to read and write. It helps children hear, identify and use different sounds that distinguish one word from another in the English language. Using phonics programmes, children are taught to read and write by directly linking phonemes (sounds in words) and graphemes (the symbols used to represent them).